In circuit design, we often overlook the basics—especially when they feel familiar.
PNP and NPN transistors are widely used. But many engineers don’t fully understand when or how to use them correctly.
Let’s uncover PNP and NPN secrets that go beyond datasheets and help in real-world design.
What Makes PNP and NPN Different?
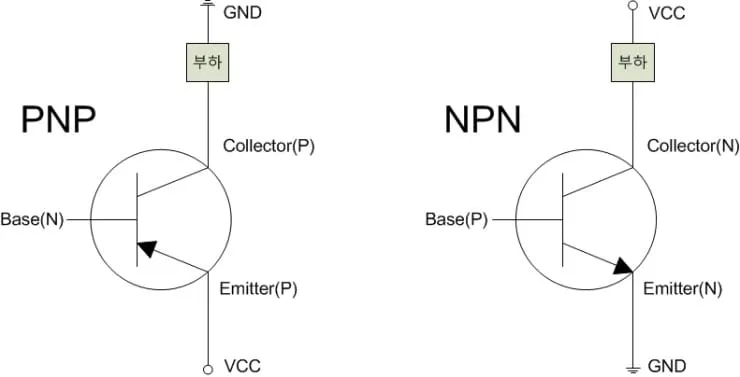
Both PNP and NPN transistors fall under the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) category.
However, their structure and current flow are different.
- NPN transistors turn on when the base is high. Current flows from the collector to the emitter.
- PNP transistors activate when the base is low. Current flows from the emitter to the collector.
This small difference affects how they work in your circuit.
4 Must-Know Secrets About PNP and NPN
1. Polarity Matters
Use NPNs with ground-side signals. They’re perfect for digital logic.
PNPs work better for high-side switching, such as in automotive systems.
2. Switching Speed
NPN transistors switch faster. That’s why engineers often prefer them in high-speed circuits.
PNPs work fine but need pull-up resistors and other drivers.
3. PCB Layout Impacts
Placing PNPs on the high-voltage side can make board design harder.
NPNs, placed near ground, offer more flexibility and easier routing.
4. No Direct Swap
You can’t just replace one with the other.
Each type needs different logic and wiring. Swapping requires a redesign.
When Should You Use PNP or NPN?
Choose NPN if you want:
- Easy control from microcontrollers
- Fast switching
- Ground-referenced design
Choose PNP if you need:
- High-side switching
- Specific industrial standards
- Load to remain grounded when off
Understanding your power rails and signal flow helps you pick the right type.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between PNP and NPN isn’t about which is better. It’s about using the right part for your circuit.
By applying the PNP and NPN secrets shared here, you’ll build faster, safer, and more efficient designs.
When something doesn’t work as expected, step back and ask: did I choose the right transistor?

Leave a Reply