Understanding RMS Voltage: The True Value of AC Power
When we talk about voltage in AC (alternating current) circuits, we often throw around terms like “peak voltage” or “average voltage.” But there’s one term that really matters when it comes to power calculations—RMS Voltage, or Root Mean Square Voltage. This is the “effective” voltage that does the same work as a DC voltage of the same value. In this post, we’re going to break down what RMS voltage actually means, how it’s calculated, and why it’s so useful. We’ll also work through three example problems ranging from basic to advanced level.
What Does RMS Voltage Mean?
RMS stands for Root Mean Square. It’s a statistical way of expressing the “effective” value of a varying voltage or current. In the case of AC voltage, which fluctuates sinusoidally, the RMS value is the equivalent DC voltage that would deliver the same power to a resistive load.
Let’s say you have a sinusoidal AC voltage described by:
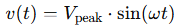
The RMS voltage is calculated using:
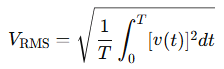
For a pure sine wave, this simplifies to:
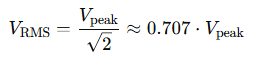
So if your wall outlet provides 220V RMS, that actually corresponds to a peak voltage of:
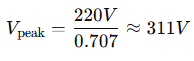
Why Is RMS Important?
RMS values are used in most electrical specifications. Multimeters measure RMS values, your home receives RMS voltage, and power formulas in AC circuits use RMS values:
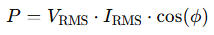
Without RMS, comparing AC to DC would be like comparing apples to oranges.
RMS Voltage vs Peak and Average

The average of a sine wave over a full cycle is zero, so it’s not useful for calculating power.
🟢 Beginner Level
Problem:
A sine wave has a peak voltage of 10V. What is the RMS voltage?
Solution:
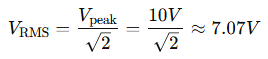
✅ Answer: 7.07V
🟡 Intermediate Level
Problem:
An AC power source provides 230V RMS to a resistive heater that consumes 2.3 kW of power. What is the resistance of the heater?
Solution:
We know:
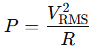
Rearranged:
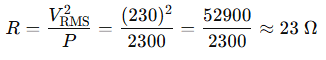
✅ Answer: 23 ohms
🔴 Advanced Level
Problem:
An AC voltage is described by:
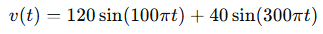
Calculate the RMS voltage of this signal.
Solution:
This signal has two sinusoidal components. For RMS, we add the square of each component’s RMS value (assuming they’re orthogonal):
First, calculate individual RMS:
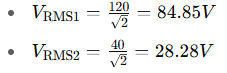
Now total RMS:
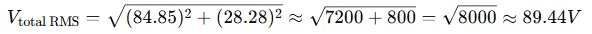
✅ Answer: 89.44V
Final Thoughts
RMS voltage is the industry standard for measuring and comparing AC signals. Whether you’re calculating power, setting voltage ratings, or designing equipment, RMS is the number that matters. It tells you how much actual work your AC voltage can do.
When you’re dealing with mixed signals, harmonics, or anything beyond a simple sine wave, knowing how to properly calculate RMS ensures you’re not underestimating or overloading your components.
Thevenin and Norton : Proven Method to Solve Any Circuit
Millman’s Theorem Made Simple with 3 Solved Circuit Problems

Leave a Reply