Understanding Reactive Voltage: The Hidden Side of AC Power
When we talk about electricity in AC circuits, most people focus on voltage, current, and power—especially how much power gets consumed. But not all power is created equal. In fact, there’s a special type of voltage and power that doesn’t do any “real work,” but still flows in your circuit. That’s reactive voltage, and it plays a critical role in how AC systems behave.
In this post, we’ll explore what reactive voltage is, how it’s different from active (real) voltage, why it matters, and how to calculate it. We’ll also walk through three example problems to build your understanding step by step.
🔌 What Is Reactive Voltage?
Reactive voltage is associated with the energy exchange between inductive and capacitive elements in an AC circuit. It doesn’t produce real power—like light or heat—but it affects how current and voltage interact in the system.
In simple terms, reactive voltage is the voltage component that exists due to reactance (not resistance), especially in inductors and capacitors. It causes current to lead or lag the voltage.
⚡ Real, Reactive, and Apparent Power
Let’s break this down:
- Real Power (P): Measured in watts (W), this is the power that actually performs work.
- Reactive Power (Q): Measured in volt-amperes reactive (VAR), this is the power stored and released by reactive components.
- Apparent Power (S): Measured in volt-amperes (VA), this is the vector sum of real and reactive power.
The relationship is often visualized in a power triangle:
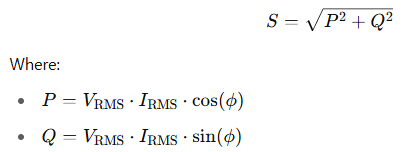
Here, ϕ is the phase angle between voltage and current.
🌀 Where Does Reactive Voltage Come From?
Reactive voltage appears across inductors and capacitors, which store energy temporarily and then release it back into the circuit. Unlike resistors, which consume power, these elements don’t use up the energy—they simply delay it.
For an inductor, the voltage leads the current:
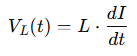
For a capacitor, the current leads the voltage:
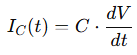
This lead-lag behavior causes a phase shift, which creates reactive power.
🤷 Why Does Reactive Voltage Matter?
Reactive voltage:
- Does not do useful work, but still requires capacity in generators and wires.
- Impacts voltage regulation—too much reactive power can drop voltage levels.
- Must be managed, especially in power distribution, to maintain system stability.
That’s why electric utilities charge for power factor correction if your system draws too much reactive power.
🔍 Common Reactive Voltage Formulas
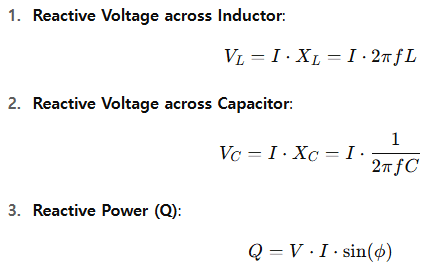
🟢 Beginner Level
Problem:
An inductor with an inductance of 50 mH carries an RMS current of 2 A at 60 Hz. What is the reactive voltage across the inductor?
Solution:
Use the formula:
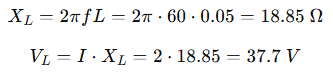
✅ Answer: 37.7 V (RMS)
🟡 Intermediate Level
Problem:
A capacitor with a capacitance of 100 µF is connected to a 50 Hz supply. If the RMS current is 3 A, what is the reactive voltage across the capacitor?
Solution:
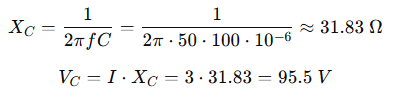
✅ Answer: 95.5 V (RMS)
🔴 Advanced Level
Problem:
An AC circuit has a voltage of 240V RMS and current of 10A RMS with a power factor of 0.8 lagging. Calculate the reactive voltage component contributing to reactive power.
Solution:
First, calculate reactive power:
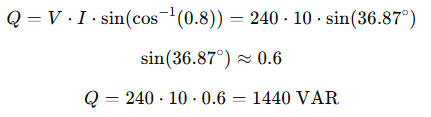
To get reactive voltage component:
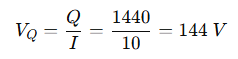
✅ Answer: 144 V (Reactive Voltage)
🧠 Summary
Reactive voltage is a fundamental concept in AC power systems. Even though it doesn’t do “real” work like powering a light bulb or heating a toaster, it still moves through the circuit and affects performance.
- It arises from inductors and capacitors.
- It causes phase shifts between voltage and current.
- It leads to reactive power (Q) that burdens power lines and generators.
- Managing reactive power is critical for power quality and efficiency.
If you’re working with motors, transformers, or AC power systems, ignoring reactive voltage isn’t an option.
Understanding RMS Voltage: The True Value of AC Power
Thevenin and Norton : Proven Method to Solve Any Circuit
Millman’s Theorem Made Simple with 3 Solved Circuit Problems

Leave a Reply