Ohm’s Law: Intermediate-Level Understanding
While the basic formula ![]() introduces the core relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, applying Ohm’s Law in real-world scenarios requires a deeper understanding of how this law interacts with more complex electrical and electronic systems.
introduces the core relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, applying Ohm’s Law in real-world scenarios requires a deeper understanding of how this law interacts with more complex electrical and electronic systems.
1. Ohm’s Law in Series and Parallel Circuits
In multi-element circuits, resistance behaves differently depending on configuration:
- Series Circuit:
Total resistance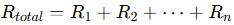
Current is the same through all elements, so voltage divides according to resistance.
- Parallel Circuit:
Total resistance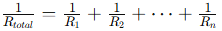
Voltage across all branches is the same, while current splits.
Ohm’s Law is applied to individual elements in such configurations, often in conjunction with Kirchhoff’s Laws for complete analysis.
2. Ohm’s Law and Power Calculation
By combining Ohm’s Law with the power equation ![]() , we can derive:
, we can derive:
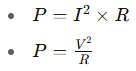
These variations help engineers calculate power dissipation in resistive components — a crucial factor in thermal design and component sizing.
3. Temperature Effects on Resistance
Real-world resistors are not always ideal. Resistance changes with temperature, especially in materials like metals. This is described by:
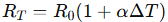
Where:

This makes Ohm’s Law non-linear under varying thermal conditions — an important factor in high-power or precision circuits.
4. Limitations with Non-Ohmic Devices
Ohm’s Law is only valid for ohmic materials — components whose current-voltage relationship is linear and passes through the origin. However, many real-world components are non-ohmic, such as:
- Diodes
- Transistors
- LEDs
- Zener diodes
For these, V is not proportional to I, and Ohm’s Law cannot be applied directly. Instead, characteristic curves (I-V curves) or nonlinear models must be used.
5. Ohm’s Law in Circuit Simulation and Design
In circuit simulation tools like SPICE, Ohm’s Law forms the foundation for node-voltage and mesh-current analysis. Engineers often use Ohm’s Law:
- To calculate voltage drops across elements
- To size current-limiting resistors
- To estimate thermal load and energy consumption
- To design voltage dividers and biasing networks
These calculations are embedded in larger design systems, but a strong grasp of Ohm’s Law remains essential for manual verification and intuition.
Final
At the intermediate level, Ohm’s Law is no longer just a simple equation — it becomes a tool for modeling, analyzing, and optimizing real-world systems. Understanding its limitations and how it integrates with more advanced concepts is critical for designing reliable and efficient electrical and electronic circuits.

Leave a Reply