What is Bimetal?
Bimetal consists of two different metals bonded together, each having distinct thermal expansion coefficients. This unique combination causes the bimetal strip or component to bend or flex predictably when temperature changes occur. The difference in expansion rates between the metals generates mechanical movement, which many devices use efficiently.
Engineers commonly combine steel with copper, brass, or nickel. They carefully select each pair to optimize performance according to the required temperature range, mechanical strength, and response speed.
How Does Bimetal Work?
Bimetal works by utilizing thermal expansion differences. As temperature rises, one metal expands faster than the other, making the strip curve. When the temperature decreases, the strip returns to its original shape. This bending triggers switches or controls in devices such as thermostats and circuit breakers. Because it relies on physical properties, bimetal offers precise and reliable temperature control without complex electronics.
For example, a thermostat uses the bending motion of the bimetal strip to open or close an electrical circuit. This simple mechanism effectively controls heating or cooling systems, requiring no external power and enhancing energy efficiency.
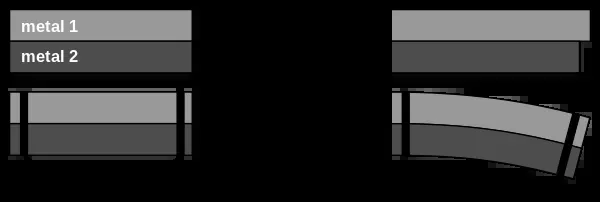
Advantages of Bimetal
Bimetal offers many advantages. First, it provides durability by withstanding repeated thermal cycling without wear. Second, its predictable mechanical response ensures precise temperature control. Third, mechanical switching reduces the need for continuous electrical power or electronic sensors. Fourth, manufacturing and material costs stay lower compared to electronic alternatives. Finally, designers can tailor metal pairings to suit specific industrial or consumer needs.
Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturers produce bimetal strips through welding, riveting, or explosive bonding techniques. Explosive bonding creates a molecular bond between metals, enhancing adhesion strength and durability. Quality control plays a vital role in ensuring uniform bonding without defects, which maintains consistent thermal behavior. Furthermore, heat treatments and surface finishing improve mechanical properties and longevity.
Common Applications of Bimetal
Industries widely use bimetal in various applications. For instance, HVAC systems depend on bimetal strips to regulate heating and cooling operations. Automotive sensors utilize bimetal components for accurate engine and exhaust temperature monitoring. Additionally, safety devices use bimetal to prevent overheating, protecting equipment and ensuring operational safety.
Design Considerations
Designers carefully consider several factors when creating bimetal devices. They select metals with sufficient differences in thermal expansion to maximize bending effect. They also determine thickness and length to influence sensitivity and the bending range. Moreover, they evaluate environmental factors such as corrosion resistance and mechanical stress. Lastly, response time matters, as devices must react promptly to temperature changes. Thoughtful design guarantees reliable performance and durability.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Bimetal
Understanding bimetal technology empowers engineers and technicians to develop efficient and reliable temperature control devices. Bimetal combines simplicity with power, providing practical solutions across many industries. By mastering its principles, professionals can innovate and enhance safety. As industries demand more precise thermal management, bimetal remains a fundamental material in modern engineering.

Leave a Reply